Rigid PCB — Durable, Reliable, Flame-Resistant
Rigid PCB is one of the three major types of Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs), alongside Flex PCBs and Rigid-Flex PCBs, classified by the substrate’s flexibility and application needs.
What is a Rigid PCB
Rigid PCBs are made from solid and inflexible materials such as:
🔹 Phenolic resin
🔹 Epoxy resin
🔹 Polyester glass
🔹 Most commonly: FR-4
FR-4 refers to a fire-retardant material composed of epoxy resin (as a binder) and electronic-grade fiberglass cloth (as reinforcement), laminated with copper foil.

PCB Layers Available
Rigid PCBs are available in multiple layer configurations:
-
Single-Layer PCB
-
Double-Layer PCB
-
Multi-Layer PCB — up to 40+ layers
Layer count depends on the complexity of the circuit design and the requirements of the end product.
Key Benefits of Rigid PCBs
✅ Excellent Dimensional Stability
Rigid PCBs maintain their shape and do not deform under pressure or heat over their lifecycle.
🔥 Flame Resistance
-
Most rigid PCBs have a temperature resistance of up to 130°C
-
High-performance boards can resist up to 170°C
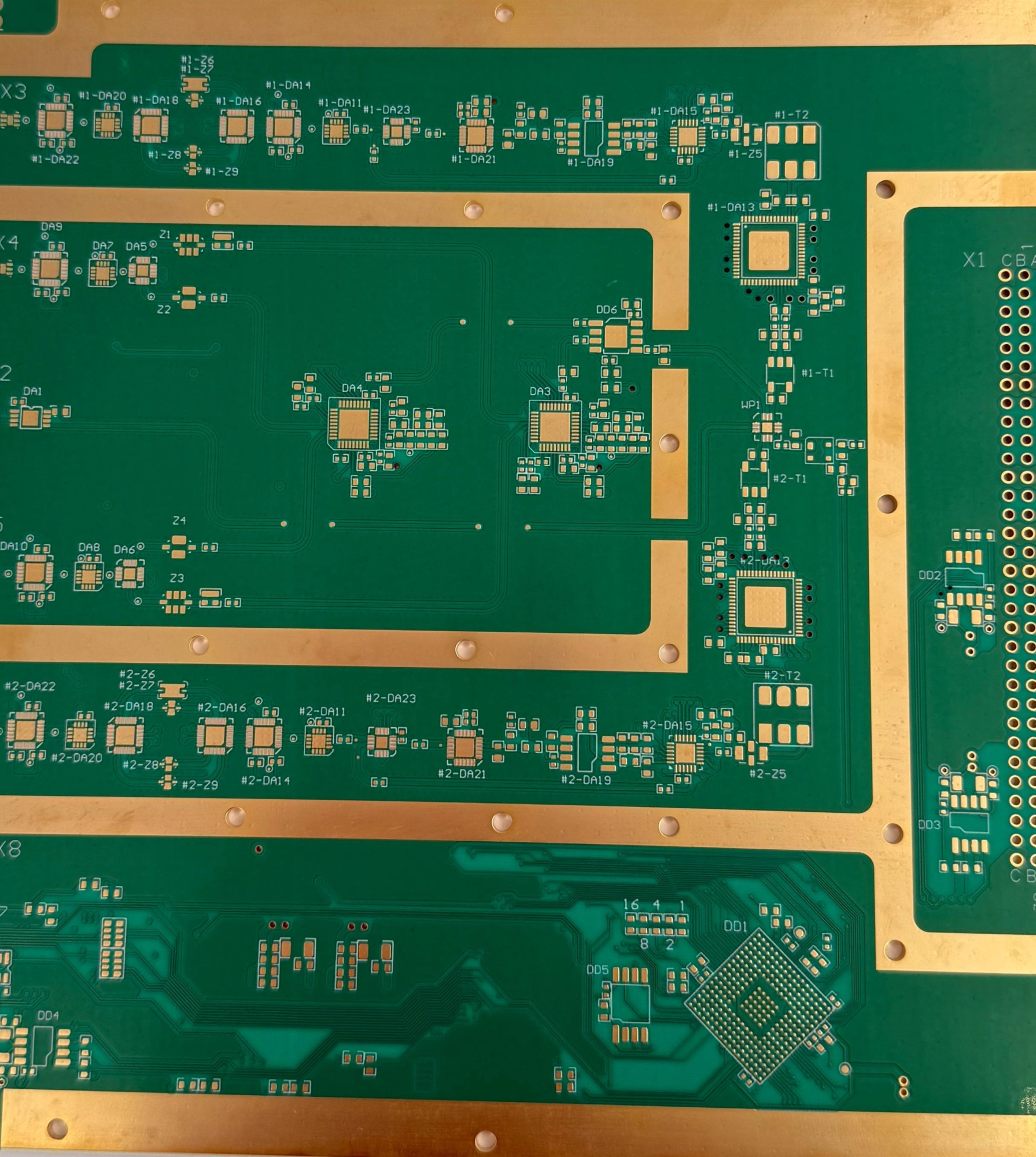
Applications of Rigid PCBs
Rigid PCBs are essential for durable electronics and core control systems. Common uses include:
-
Motherboards
-
Control boards
-
Button boards
-
Charger boards
-
Sensor boards
-
Consumer electronics


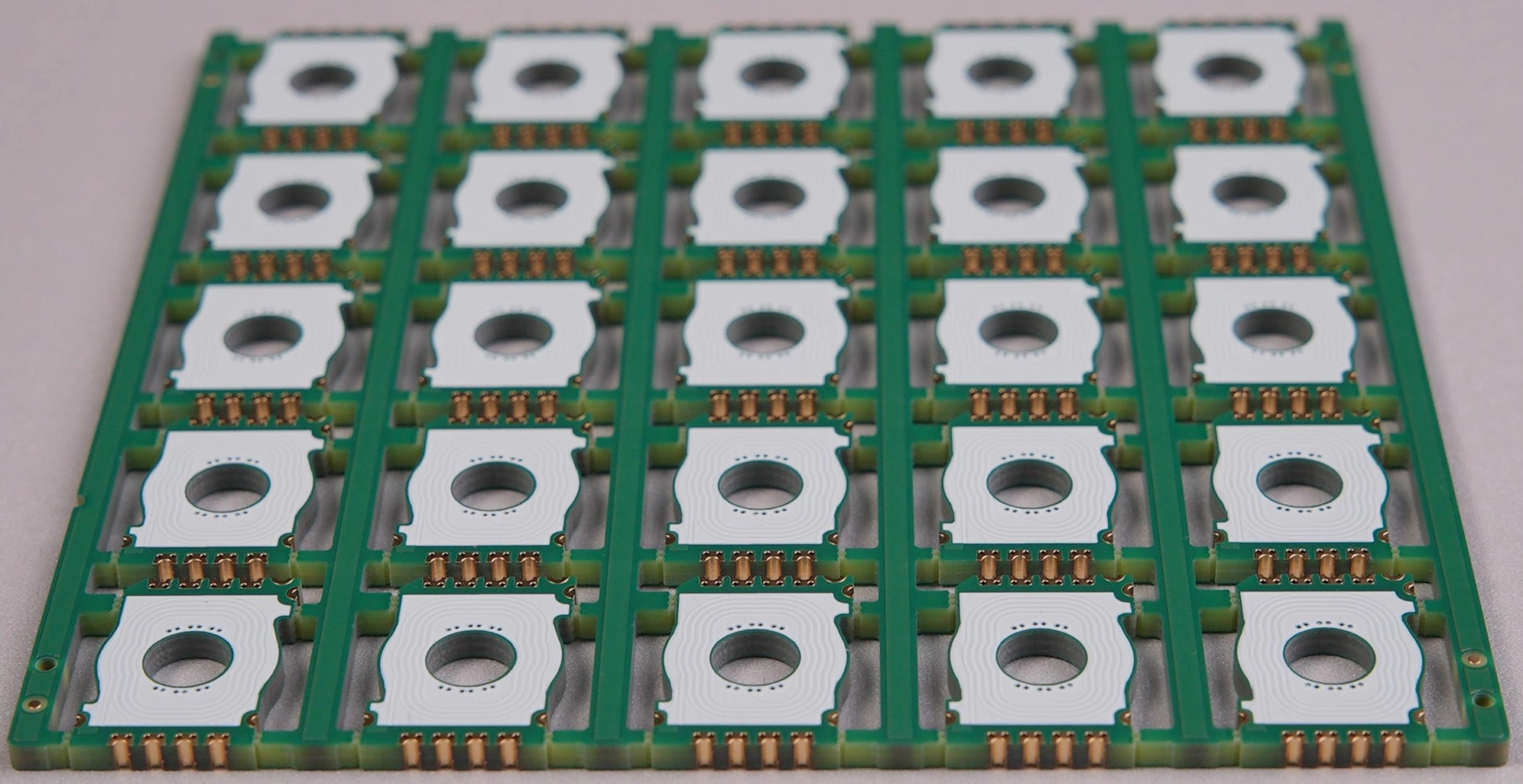
Summary
Rigid PCBs are the backbone of stable, high-performance electronic products. With:
-
Strong mechanical support
-
Flame retardant properties
-
Flexibility in layer design
-
Long product life cycles
They are ideal for high-precision and reliability-demanding applications.