Rigid-Flex PCB — The Perfect Blend of Strength & Flexibility
Rigid-Flex PCB combines the benefits of both Rigid PCBs and Flexible PCBs, providing mechanical strength where needed and flexibility in areas that require motion or tight-space connections.
What is Rigid-Flex PCB
Rigid-Flex PCB is composed of two main parts:
-
Rigid PCB Section – Provides hardness, support, and stable component mounting
-
Flex PCB Section – Offers flexibility, bending ability, and compact connections
This hybrid structure is specially designed for:
-
Space-saving layouts
-
Complex internal interconnections
-
Simplified assembly
-
Enhanced product design efficiency

Materials Used
✅ Rigid Part: Typically made from FR-4
✅ Flex Part: Common materials include:
-
-
Polyimide (PI)
-
PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone)
-
Conductive Polyester Films
-
Key Features of Rigid-Flex PCB
-
Compact & Flexible – Perfect for space-constrained or foldable designs
-
3D Design Freedom – Enables three-dimensional layouts
-
Superior Connectivity – High electrical reliability and minimal interconnect failure
-
Simplified Assembly & Testing – Fewer cables, connectors, and steps
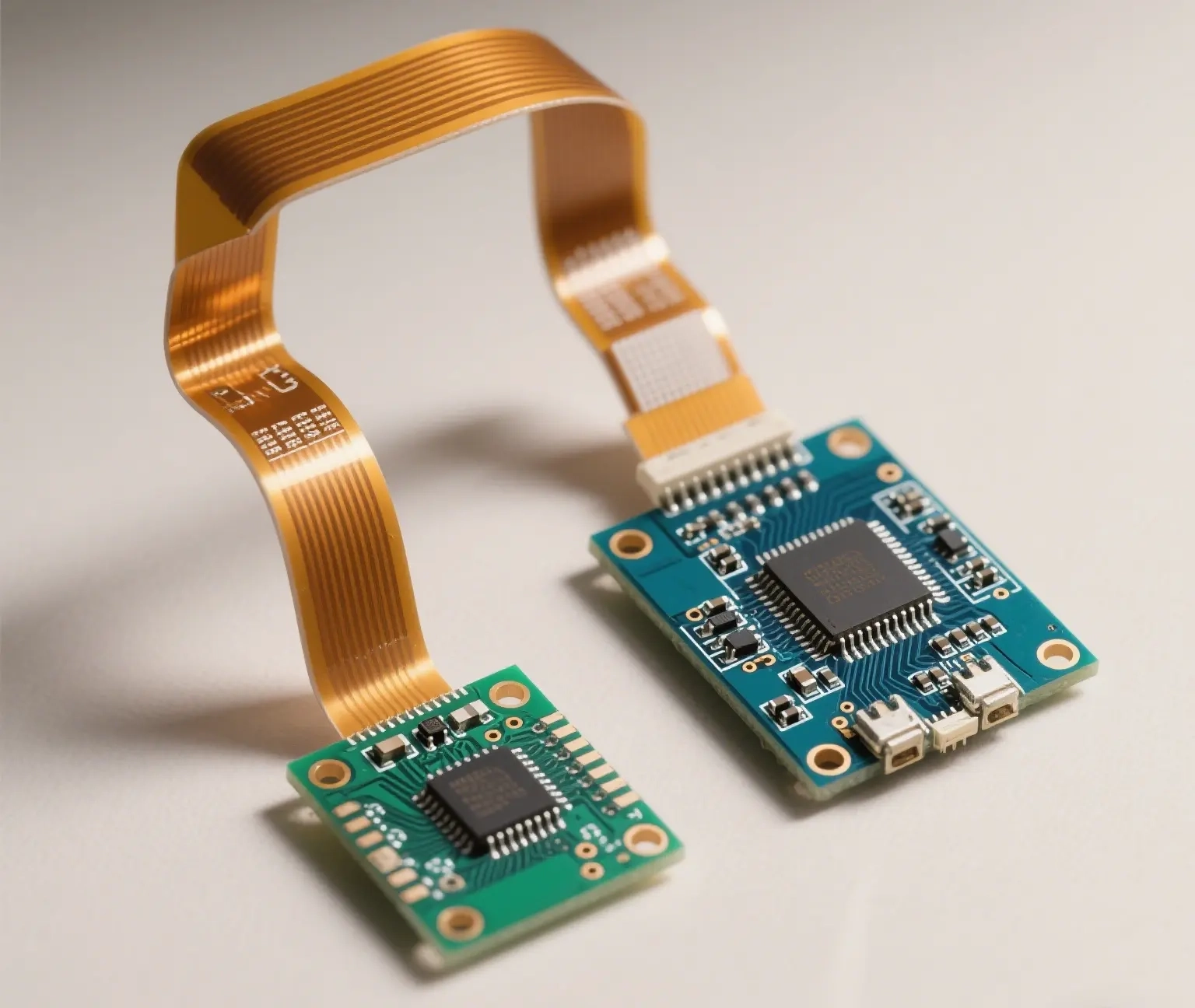
Challenges to Consider
While offering many advantages, Rigid-Flex PCBs also come with increased complexity and cost in manufacturing.
Reasons include:
-
Precision layering and lamination processes
-
Longer production cycles
-
High-performance material requirements
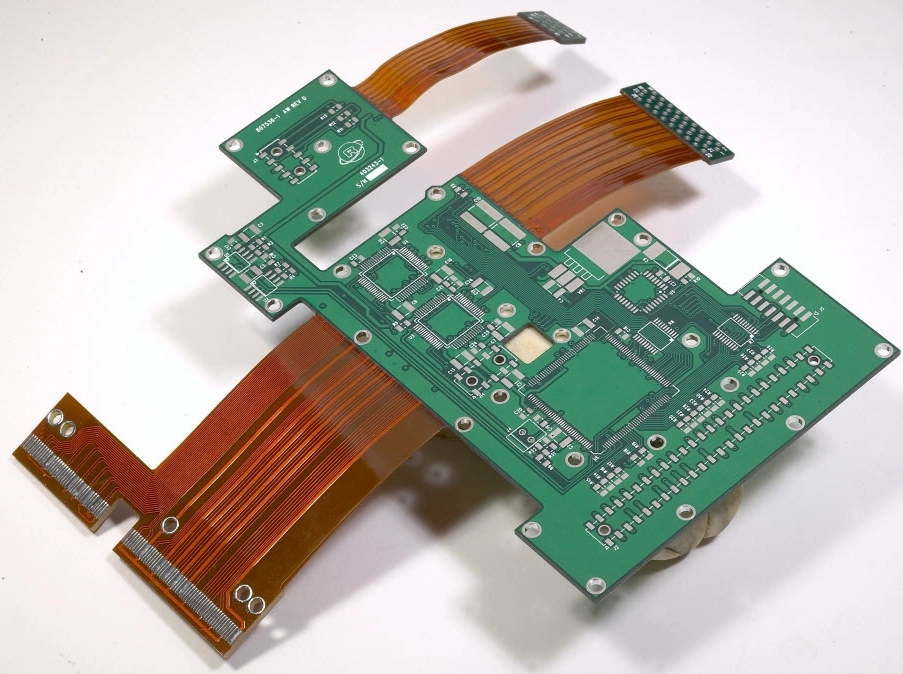
Applications of Rigid-Flex PCB
Rigid-Flex PCBs are ideal for industries that demand compact size, reliability, and mechanical durability:
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Flight control systems, sensors |
| Automotive | Camera modules, dashboard electronics |
| Consumer Electronics | Foldable phones, wearables |
| Medical Devices | Implants, diagnostic instruments |
| Telecommunications | Signal routers, handheld terminals |
Specific Examples
📱 Mobile phones
🎛️ Keyboards (press key boards)
💻 Computers and LCD screens
🖥️ Motherboards and display panels
🎵 CD Walkman and portable players