PCB Materials Overview
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) use a variety of base materials depending on their performance, thermal, and electrical requirements. Below is a comprehensive overview of commonly used PCB materials.
✅ FR-4 – The Standard Workhorse
Material: Woven fiberglass cloth + Epoxy resin
Applications: Over 90% of PCBs
Thickness: 0.2mm to 3mm
Key Features:
-
Affordable and reliable
-
Mechanically strong
-
Flame-retardant

✅ Grades of FR-4:
-
Standard FR-4 – For general multilayer boards
-
High Tg FR-4 – >170°C glass transition temp
-
Low loss FR-4 – Optimized for RF
-
High temp FR-4 – Up to 280°C solder resistance
-
Halogen-free – Eco-friendly, low smoke
-
High CTE – Reduced thermal stress
-
High flex – For dynamic bending
-
Low Dk – Enhanced signal performance
📶 Rogers – High-Frequency Performance
Material: Ceramic composite laminate
Applications: Aerospace, defense, telecom, medical
Advantages:
-
Low dielectric constant variation
-
Excellent signal integrity
-
Great thermal performance
📈 Ceramic PCB – High Reliability
Materials: Alumina (Al₂O₃), AlN, BeO, LTCC
Key Benefits:
-
High temperature & frequency performance
-
Low thermal expansion
-
Excellent insulation
-
Low signal loss
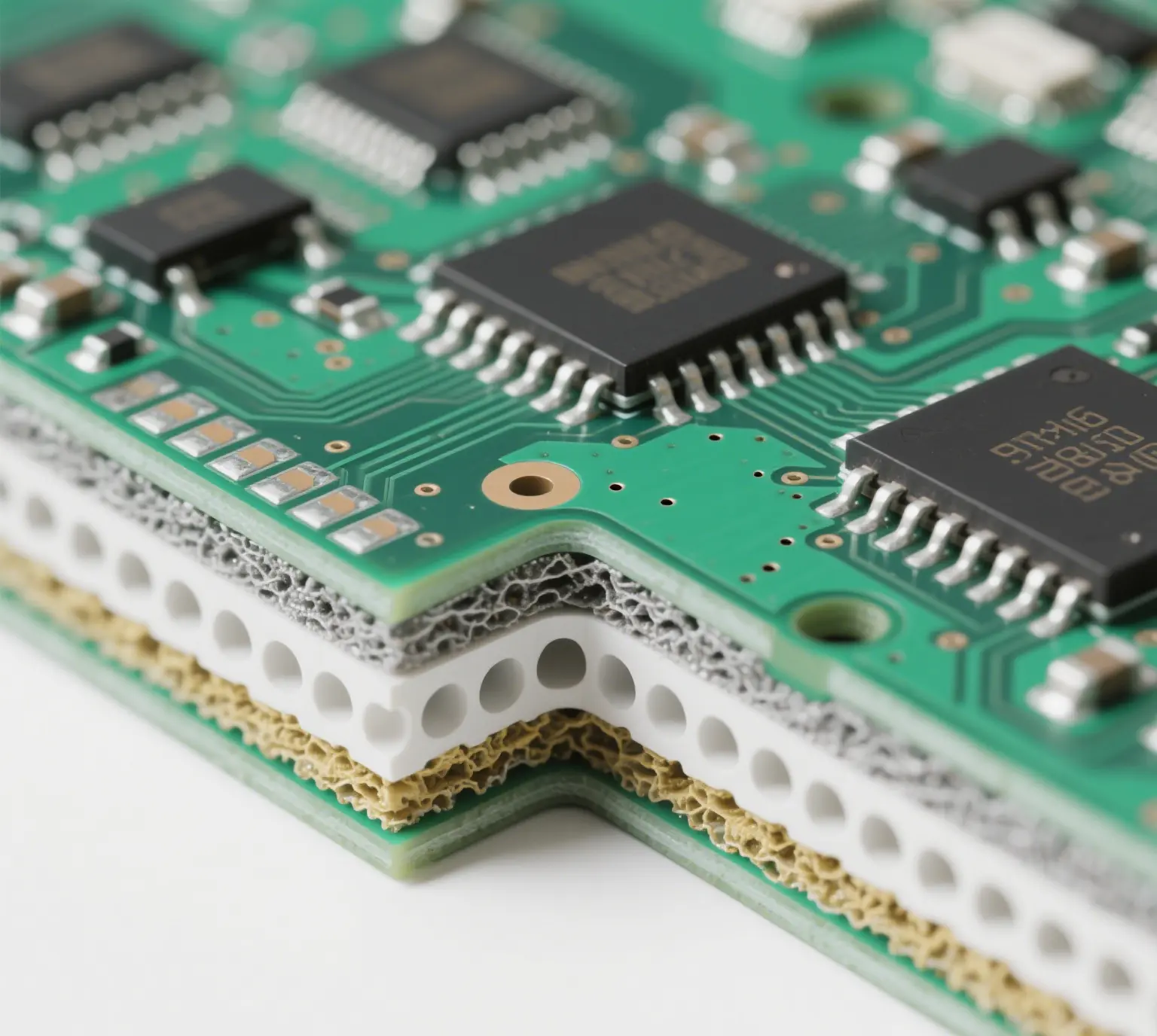
Types We Offer:
-
Alumina PCB
-
Aluminum Nitride (AlN) Base
-
Copper Clad Ceramic
Thermal Conductivity Table:
| Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) |
|---|---|
| Aluminum Nitride | 150 – 180 |
| Aluminum Oxide | 18 – 36 |
| Beryllium Oxide | 184 – 300 |
| Boron Nitride | 15 – 600 |
| Silicon Carbide | 70 – 210 |
Aluminum PCB – Heat Dissipation Champion
Advantages:
-
Lightweight, corrosion resistant
-
Excellent thermal conductivity
-
High mechanical strength
Applications: LEDs, power electronics, automotive, telecom
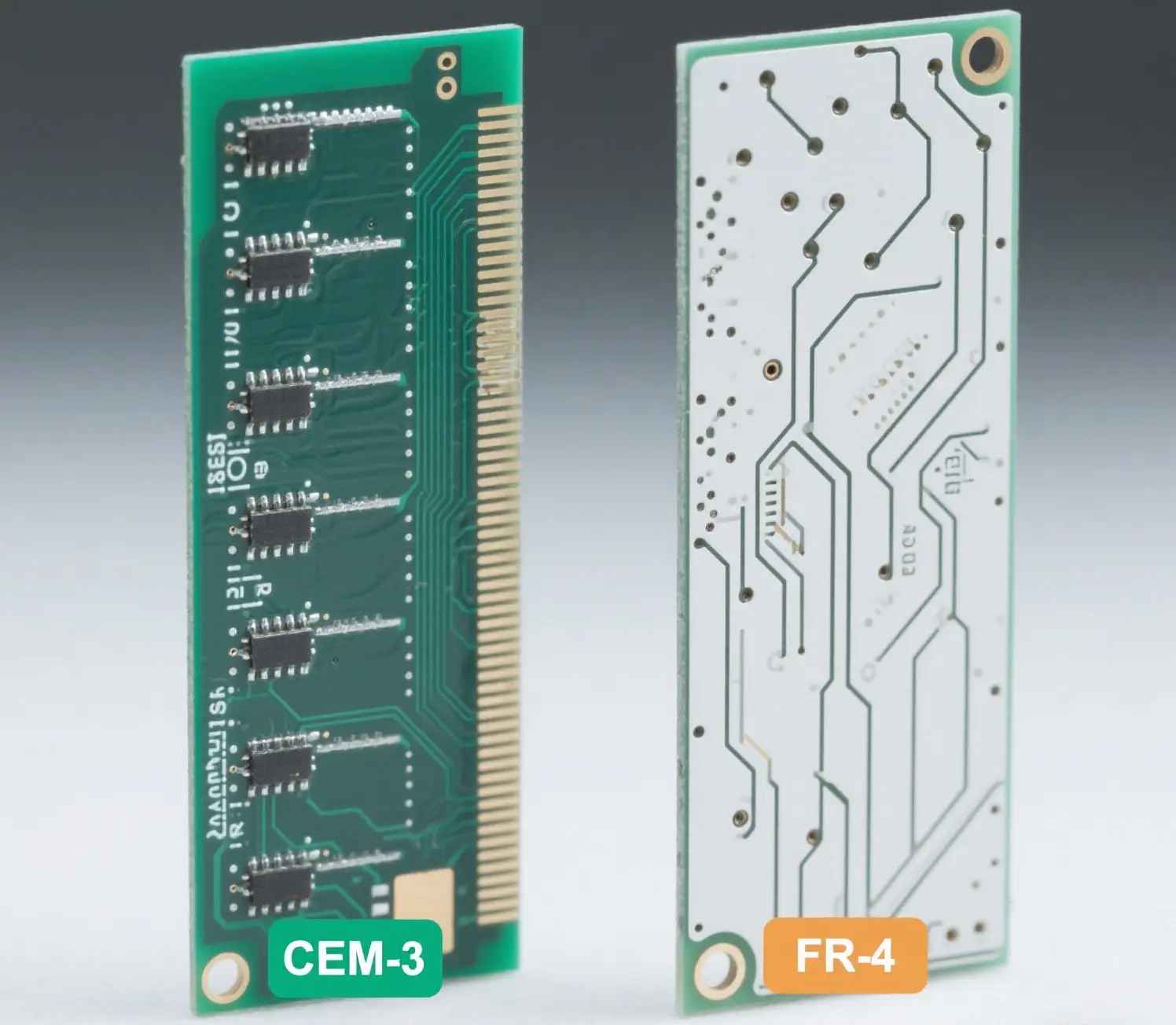
CEM-3 – Cost-Effective Alternative
Usage: High-end electronics (e.g. medical, automotive)
Pros:
-
Good mechanical & thermal stability
-
Lower cost than FR-4
Cons:
-
Higher dielectric constant
-
Lower chemical resistance

PI (Polyimide) – For Extreme Environments
Highlights:
-
Operates up to 400°C
-
Low dielectric loss
-
Excellent signal integrity
-
High thermal stress resistance
Applications: Semiconductor, aerospace, high-reliability electronics
Glass PCB – Optical Grade Precision
Usage: LED, LCD, high-precision optics
Advantages:
-
Thermal stability and homogeneity
-
UV mask etching process for precision
-
Supports fine pitch and narrow traces
Process Note:
Uses UV curable resist (positive/negative) for circuit patterning on copper-clad glass.
📌 Conclusion
Each PCB material type offers unique benefits tailored to specific applications. Choosing the right material ensures better performance, longevity, and reliability for your product.